Multi-Vehicle Linkage AGV Transfer Cart Design Introduce
Background Technique:
With the continuous development of industrial automation, in the field of mobile robots, small AGVs that are small in size, fast and flexible are needed to complete material distribution. At the same time, some large workpieces must be transported with a load capacity of more than ten tons or more. Dozens of tons of heavy-duty AGV to complete.
In the same project, the workpieces transported by AGVs are not a single product. If the AGVs are designed according to different workpieces during the design stage, multiple AGV models will need to be designed, which not only increases the difficulty of the design, prolongs the design time, but also increases the design time. Cost, and in actual project use, work efficiency will be greatly reduced, resulting in a certain waste of resources. It cannot meet the development requirements of modern industrial automation.
Technical Implementation Elements:
In order to solve the problem of low efficiency of heavy-loaded AGVs in transporting materials of different volumes, the present invention provides a control method for heavy-loaded AGVs to transport materials in a coordinated manner, so that the heavy-loaded AGVs can safely transport materials while improving work efficiency.
The technical solution adopted by the present invention to achieve the above objectives is: a heavy-duty AGV two-vehicle linkage control method, which includes the following steps:
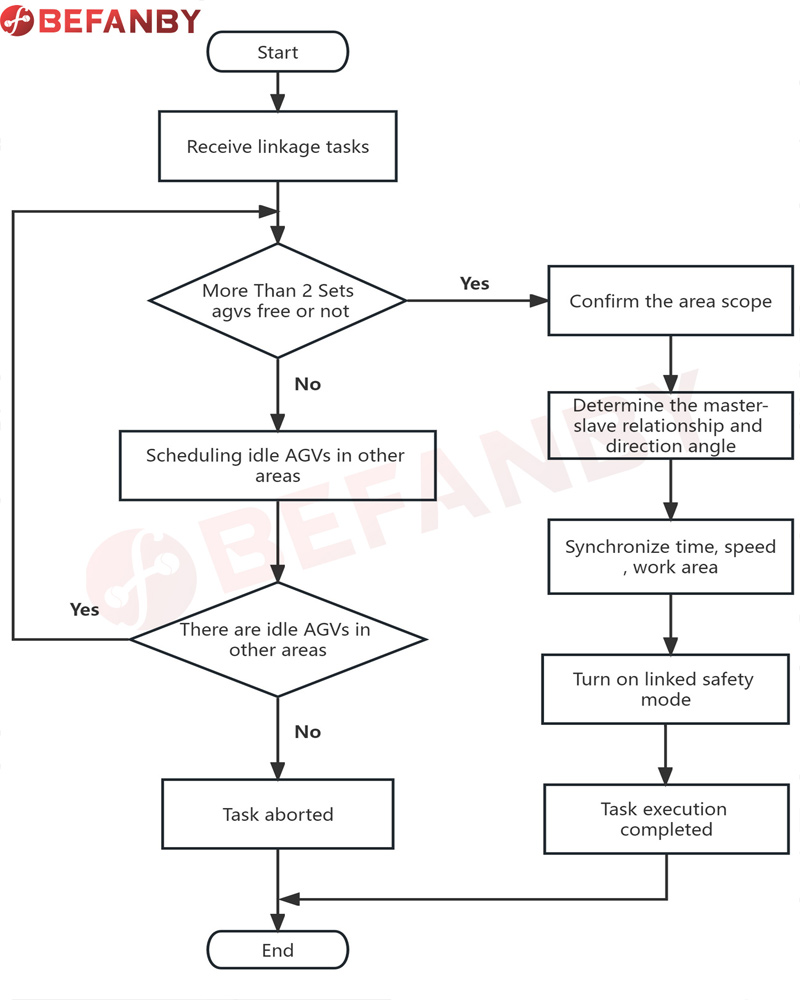
When the AGV dispatching system receives the dual-vehicle linkage task, it first determines whether there are more than two idle AGVs in the task execution area; if not, it schedules idle AGVs from other work areas. If there are no idle AGVs in other areas, the task will be terminated and a warning will be given. ;
If there are more than two idle AGVs, first dispatch the two idle AGVs closest to the task point to the task execution area, and assign the master-slave relationship; start to execute the two-vehicle linkage task, that is, the AGV dispatching system plans the driving route and driving route according to the task Time-scheduling the master vehicle and the slave vehicle to perform tasks;
After the task is executed, the slave vehicle remains stationary, and the master vehicle drives away from the task end point first. The distance between the master vehicle and the slave vehicle is greater than the set safety distance; then the master vehicle and the slave vehicle go offline respectively, and then come back online again to wait for other tasks. .
The specific distribution of the master-slave relationship is: designate one AGV as the master vehicle and the other as the slave vehicle; specify the distance and deviation angle between the two vehicles, synchronize the system time, driving speed, acceleration, and rotation angular velocity of the two AGVs, Turn on the front and rear safety distance in combination mode.
The specific combination mode is as follows: the master vehicle, the slave vehicle and the workpieces carried on the two vehicles form a combined vehicle body; the center of the combined vehicle body is set as the reference base point; when encountering a turning or lateral shift section, the reference point is The base point is the center, and the relative positions of the master vehicle and the slave vehicle are added to obtain the target movement positions of the master vehicle and the slave vehicle; the master vehicle and the slave vehicle operate according to their respective target movement positions. The center of the combined vehicle body is the center of gravity of the combined vehicle body.
When two vehicles are linked, the safe obstacle avoidance distance of the combined vehicle body is redefined, and the safety control signals of the two vehicles are shared. If there is a safety alarm in either AGV of the two vehicles, a safety alarm will be sent first, and the combined vehicle body will pass first in the traveling section.
When the linkage task is completed, the main vehicle is first released from the task and drives away from the end of the task area. After entering the safe area, the slave vehicle can be released from the task, and then the two AGVs are offline respectively, and then re-online to perform the single vehicle task.
Beneficial effects and advantages of the present invention:
The method of the present invention can improve the use efficiency of AGVs. Different types of materials are very different in volume and quality. If different types of AGVs are used for transportation, when a certain model is temporarily suspended or the structure is changed or the output is small, the transportation The use efficiency of AGVs for such materials will be greatly reduced, and the two-vehicle linkage AGV can transport materials designed according to its own model, and can also be combined with other AGVs to transport large materials, which improves AGV transportation efficiency and saves production costs.
Description of the drawings
Figure 1 Work flow chart of the heavy-duty AGV two-vehicle linkage control method of the present invention;
Detailed ways
The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and examples.
A heavy-load AGV two-vehicle linkage control method includes the following steps:
The AGV working range consists of several areas. When the console dispatching system receives a two-vehicle linkage task for transporting large workpieces, it first determines whether there are two or more idle AGVs in the assigned task point area. Find idle AGVs in each area, and when the requirements for two idle AGVs are met, the idle AGVs will be scheduled to the work area where the task is assigned.
After the AGV reaches the designated task point, the working modes of the two AGVs must be reassigned, one as the master vehicle and the other as the slave vehicle. The center point of the vehicle body in the combined mode is calculated, and the position information of each vehicle relative to the center point of the vehicle body is calculated. , synchronize the vehicle body system time, driving speed, acceleration, and rotation angular velocity.
Redefine the safe anti-collision range of the combined mode car body, share safety control signals, and increase the level of safety alarm information.
The dispatching system plans the entire driving section and the safe range of the driving section. If other AGV vehicles want to pass through this section, the priority level will be lower than the two-vehicle linkage task AGV. If they have entered the safe range, they must leave the area first to ensure Linked AGVs have priority.
When encountering turning or sideways shifting sections, in order to ensure smooth transport of materials, the speed should be limited to less than 0.2m/s and the vehicle body posture should remain consistent.
After arriving at the unloading task point, the materials are first moved to the designated work station, and the main vehicle is driven away from the road section at a safe distance, and then the main vehicle and the slave vehicle are taken off the line respectively, and then re-online respectively, ending the two-vehicle linkage task.
As shown in Figure, when the dispatching system receives a link between two vehicles, it first determines the number of idle AGVs in the task start point area. If the number is less than 2, it searches for idle AGVs from near to far. If there are not two idle AGVs, If required, the task will be terminated and unfinished task information will be prompted. If there are two or more, the two nearest idle AGVs are scheduled to arrive at the task starting point.
After the AGV arrives at the designated location, it must first reassign the working mode, with one as the master vehicle and the other as the slave vehicle. According to the set external dimensions of the material in the database, the position distance of each agv is adjusted.